What is Ovarian Cancer? Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Signs, Stages, Diagnosis
2022-09-30 / RG STONE HOSPITAL / Female Urinary Incontinence
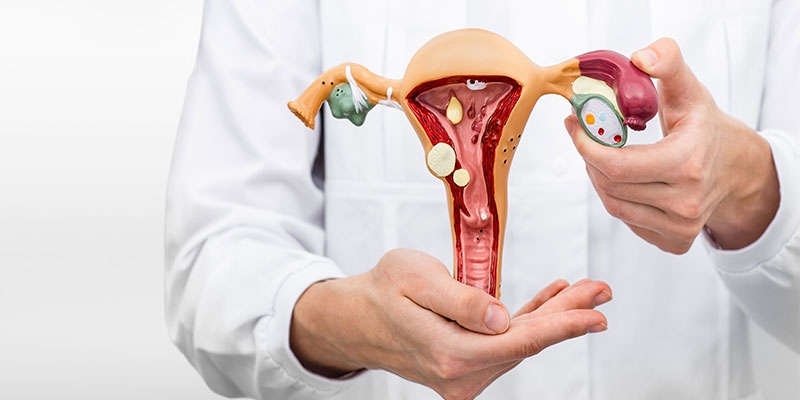
Ovarian cancer is a kind of cancer that occurs in 1 in every 75 women. Ovarian cancer is the growth of cells that form in the ovaries. The cells multiply quickly and can invade and destroy healthy body tissue. The female reproductive system contains two ovaries on each side of the uterus. The ovaries, each one of almond size and produce eggs known as “ova” along with estrogen and progesterone hormone. Ovarian cancer is usually treated by chemotherapy. It is generally not diagnosed at an early stage, only 20% of the cases are diagnosed at that stage. 97% of the patients only live for a lifespan of 5 years post detection of cancer.
When ovarian cancer first occurs, it may not cause any noticeable symptoms. When symptoms of ovarian cancer appear, they are usually attributed to other, more common conditions. General signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer are:
-Constipation
-Bloating
-Pain in the Abdominal region
-Difficulty In Eating
-Urinary Incontinence like increased urge and frequency to pee
-Discomfort in the pelvic area
-Malaise
-changes in bowel habits such as constipation
-Frequent urination
Some more symptoms are fatigue, tiredness, pain while sexual transmission, irregular periods, and back pain.
Ovarian cancer is the second most common cancer in females. It occurs most commonly between the age group of 50 to 65 years, but can occur in younger and older people as well. For people with ovaries, the lifetime risk of developing ovarian cancer is about 1.4%.
There are many different types of cancer that originate in the ovaries. The most common is called epithelial ovarian cancer (the word "epithelial" refers to the type of cell). This topic overview describes the diagnosis and staging of epithelial ovarian cancer.
Risk factors of ovarian cancer:
Certain factors increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer like:
-Early (before age 12) or late (after age 52) menstruation due to menopause.
-A family history of ovarian, breast, or endometrial cancer, especially if the person has inherited a specific type of genetic abnormality called her BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation.
-A family history of a genetic disorder called Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer [HNPCC]).
How to lower the risk of ovarian cancer:
In addition to the basics of a healthy lifestyle like eating healthy, exercising, and maintaining target weight, the following factors reduce the risk of ovarian cancer:
-Pregnancy: The more pregnancies a woman has, the lower her risk of ovarian cancer.
-Oral contraception: The longer a woman takes oral contraceptives, the more effective they are at preventing the development of ovarian cancer. This protection seems to last for years after the last pill. However, oral contraceptives also come with some risks, so you should consult your doctor to determine if this is a good choice for you.
-Tubal ligation: Tying "fallopian tubes" can lower the risk of ovarian cancer, but MSK experts say the surgery should be aimed at preventing pregnancy, not at reducing ovarian cancer risk. emphasized.
Diagnosis of ovarian cancer:
Blood tests and scans are usually done first, but other tests are often needed to diagnose ovarian cancer.
An ultrasound may be done to check for abnormalities in the ovaries. This can be done by inserting a scanner (finger size) into the vagina (transvaginal scanning). Alternatively, there is an external scan of the abdomen (abdominal scan).
If the scan returns to normal and symptoms persist for more than a month she should see her GP again. Especially after menopause, sometimes the ovaries are too small to show up on the scan. Other tests you may have are:
-CT scan
-Taking a small sample of cells or fluid from the ovaries (needle biopsy),
-Viewing the ovaries with a camera at the end of the tube through a small incision in the abdomen (laparoscopy)
-Surgery to remove tissue or sometimes ovaries (laparotomy)
Ovarian cancer is common cancer in women with no evident symptoms, we advise all women especially after the age of 50 years to get their regular screening done. We at RG Hospital have highly experienced doctors who have proven experience in treating ovarian cancer. In case of an emergency visit them to get the best treatment.
Categories
Hernia Repair
Appendicitis
Piles
Urological Treatment
Hernia treatment
Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
Gall Bladder Stone
Urinary / Kidney Stone
Vitamins
Indian Health Care System
Exercise
Obesity
Female Urinary Incontinence
Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery (SILS)
Kidney Cancer
Bladder Cancer
Ovarian cancer
Nephrology
Bariatric Surgery
Kidney Function Test
Female Urology
Radiation Therapy
Alcoholic Fatty Liver
Liver disease
Gastroenterology
Kidney Disease
Nutrition & Health
Lung Cancer

