What is Ectopic Pregnancy?
2022-01-10 / RG STONE HOSPITAL / Urological Treatment
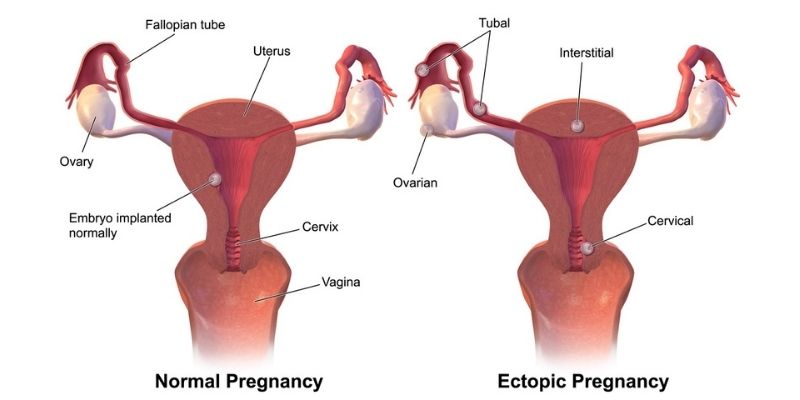
During a normal pregnancy the fertilized egg implants and grows in the uterus, ultimately giving you the most joyous day in your life when your baby is born. However, in an ectopic pregnancy the egg implants outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes giving rise to an uncommon condition. Ectopic pregnancies are also known as "tubal pregnancies" since fallopian tubes are involved. In addition to the ovary, the egg might implant in the abdomen or the cervix.
Nonetheless, there isn't enough room or living tissue in any of these places to support a pregnancy. Therefore, as the fetus develops, the organ that houses it will finally rupture. This can result in significant bleeding, putting the mother's life in jeopardy. As a result, a live birth is not possible with a classic ectopic pregnancy.
What causes an Ectopic Pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg is unable to travel down the fallopian tube to the uterus in a timely manner. An infection or inflammation can cause the tube to become clogged. The tube can get clogged as a result of:
- Inflammation of the pelvis (PID).
- Endometriosis is a condition in which cells from the uterine lining implant and develop elsewhere in the body.
- Previous abdominal or fallopian procedures have left scar tissue.
- Occasionally, congenital abnormalities can alter the tube's form.
What are the Signs and Symptoms?
Ectopic pregnancy symptoms are the same as normal pregnancy symptoms in the first few weeks, such as missed periods, exhaustion, nausea, and aching breasts.
The following are the main symptoms of ectopic pregnancy:
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
- Vaginal bleeding
If you have these symptoms and believe you are pregnant, consult your doctor immediately.
How is Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
If you don't have any of the signs of a fallopian tube rupture, but your ob-gyn or other health care provider feels you might be pregnant, he or she may:
- Examine your pelvis
- To see how the pregnancy is progressing, even ask you to get an ultrasound.
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a pregnancy hormone. The doctor can detect HCG levels in ectopic pregnancy.
What is the Treatment for an Ectopic Pregnancy?
Because an ectopic pregnancy cannot migrate to the uterus or be relocated to the uterus, it must be treated. The treatment of ectopic pregnancy consists of two methods: medication or surgery. Each ectopic pregnancy surgery necessitates several weeks of follow-up
Can you conceive again after an Ectopic Pregnancy?
Depending on the therapy you received and the status of your fallopian tubes, most people who have had an ectopic pregnancy can have safe pregnancies later. It may be more difficult to conceive if one of your fallopian tubes has been removed or if it is damaged. You're more likely to have another ectopic pregnancy if you've had one already.
Conclusion
If you think you might be at risk for an ectopic pregnancy, consult your doctor before continuing the pregnancy to discuss your alternatives. Talk to your doctor if you're pregnant and worried about an ectopic pregnancy, since it's critical to detect it early for the mother’s health. To verify that your pregnancy is progressing appropriately, visit the nearest RG Stone Hospital to examine your hormone levels or schedule an early ultrasound.
Categories
Hernia Repair
Appendicitis
Piles
Urological Treatment
Hernia treatment
Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
Gall Bladder Stone
Urinary / Kidney Stone
Vitamins
Indian Health Care System
Exercise
Obesity
Female Urinary Incontinence
Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery (SILS)
Kidney Cancer
Bladder Cancer
Ovarian cancer
Nephrology
Bariatric Surgery
Kidney Function Test
Female Urology
Radiation Therapy
Alcoholic Fatty Liver
Liver disease
Gastroenterology
Kidney Disease
Nutrition & Health
Lung Cancer

