Kidney cancer, a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the kidneys, can develop due to various factors. The primary causes include smoking, obesity, high blood pressure, and exposure to certain chemicals. Additionally, genetic predisposition and a family history of kidney cancer can increase the risk. Other contributing factors may include long-term dialysis treatment. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for early detection and prevention.
Diagnosing kidney cancer typically involves a combination of imaging tests and biopsy procedures. Initial steps often include a thorough physical examination and detailed patient history review. Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI help identify suspicious areas within the kidneys. If a tumor is detected, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the cancer's type and stage. Blood tests and urine analysis can also provide additional information about kidney function and overall health, guiding the treatment plan. Early diagnosis is key to successful treatment outcomes and improved patient prognosis.
Procedures & Interventions
Nephrectomy, either partial or radical, aims to eliminate the cancerous tissue while preserving kidney function as much as possible.
i) Partial Nephrectomy: This surgery involves removing only the tumor and a small margin of healthy tissue around it. It's often used for smaller tumors and aims to preserve as much kidney function as possible.
ii) Radical Nephrectomy: In this procedure, the entire kidney, along with surrounding tissue and possibly nearby lymph nodes, is removed. It's commonly used for larger tumors or when cancer has spread beyond the kidney.
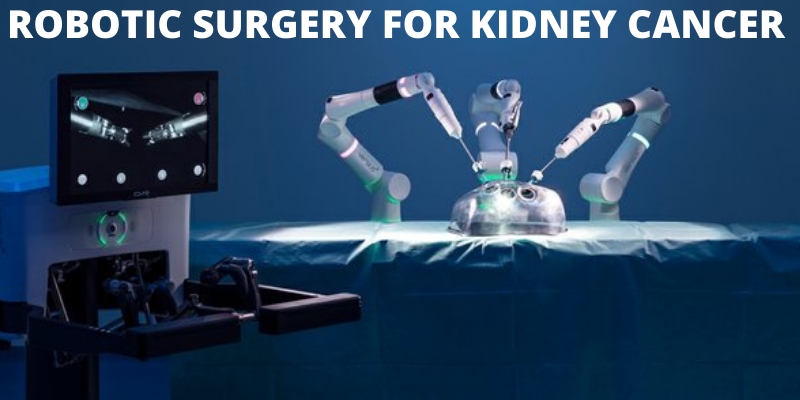
iii) Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery: These minimally invasive techniques involve making small incisions and using specialized instruments or robotic systems to perform the surgery. They offer benefits like reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
This minimally invasive treatment uses extreme heat or cold to destroy cancer cells. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and Cryoablation are effective for small tumors and can be performed with minimal impact on surrounding tissues.
These drugs specifically target cancer cells' growth and survival mechanisms, sparing normal cells. By interfering with specific molecules involved in tumor growth, targeted therapies can be more effective and less toxic than traditional chemotherapy.
This treatment boosts the body's immune system to fight cancer. Checkpoint inhibitors and other immunotherapeutic agents help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively, offering hope for advanced kidney cancer patients.
While not commonly used as the primary treatment for kidney cancer, radiation therapy can help control symptoms and reduce the size of tumors, particularly when surgery is not an option or in metastatic cases.
Though less effective for kidney cancer compared to other cancers, chemotherapy may be used in combination with other treatments for advanced cases. It involves using drugs to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells throughout the body.
For small, slow-growing tumors, particularly in older patients or those with other health issues, active surveillance involves closely monitoring the cancer without immediate treatment, intervening only if the tumor shows signs of progression.

Nephrectomy, either partial or radical, aims to eliminate the cancerous tissue while preserving kidney function as much as possible.
i) Partial Nephrectomy: This surgery involves removing only the tumor and a small margin of healthy tissue around it. It's often used for smaller tumors and aims to preserve as much kidney function as possible.
ii) Radical Nephrectomy: In this procedure, the entire kidney, along with surrounding tissue and possibly nearby lymph nodes, is removed. It's commonly used for larger tumors or when cancer has spread beyond the kidney.
iii) Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery: These minimally invasive techniques involve making small incisions and using specialized instruments or robotic systems to perform the surgery. They offer benefits like reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery compared to traditional open surgery.

This minimally invasive treatment uses extreme heat or cold to destroy cancer cells. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and Cryoablation are effective for small tumors and can be performed with minimal impact on surrounding tissues.

These drugs specifically target cancer cells' growth and survival mechanisms, sparing normal cells. By interfering with specific molecules involved in tumor growth, targeted therapies can be more effective and less toxic than traditional chemotherapy.

This treatment boosts the body's immune system to fight cancer. Checkpoint inhibitors and other immunotherapeutic agents help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively, offering hope for advanced kidney cancer patients.

While not commonly used as the primary treatment for kidney cancer, radiation therapy can help control symptoms and reduce the size of tumors, particularly when surgery is not an option or in metastatic cases.

Though less effective for kidney cancer compared to other cancers, chemotherapy may be used in combination with other treatments for advanced cases. It involves using drugs to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells throughout the body.

For small, slow-growing tumors, particularly in older patients or those with other health issues, active surveillance involves closely monitoring the cancer without immediate treatment, intervening only if the tumor shows signs of progression.
Team of Excellence
Behind every recovery story at RG Hospitals is a team of exceptional doctors whose passion for healing and innovation continues to transform healthcare and redefine patient outcomes.
Find a DoctorLooking for an Expert
RG Hospitals is proud to be the home of some of the world's most distinguished doctors.

Patient Stories
View AllPatient Testimonial | Commitment To Care
Treated by Dr. Manoj Gupta , RG Stone Hospital, Dehradun
- All Locations
- New Delhi
- Haryana
- Punjab
- Kolkata
- Chennai
- Mumbai
- Goa
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttarakhand